top of page

Water For Life
select the best..
PROPERTIES OF
ELECTROLYZED REDUCED WATER
Alkline
pH (Potential Hydrogen)

In the chemistry of electrolysis, by convention, the positively charged hydrogen (H+) ions flow towards the anode while the negatively charged hydroxyl (OH-) ions flow towards the cathode. Consequently, electrolysis separates these constitute the “acid” component of the water and the hydroxyl (OH-) ions make up the “alkaline” component.
The term pH stands for “potential Hydrogen”. The more hydrogen (H +) ions are concentrated in a solution, the more acidic it is. While the full pH scale range is from 0 to 14, anything below a pH of seven is considered acidic and anything above seven is considered alkaline (or basic).
In the human body, pH is critical, especially in your blood. The pH range that is considered to be normal for blood is between 7.30 and 7.45. Blood pH is a direct indicator of how much oxygen is available for your cells. Blood at a pH of 7.45 contains 65% more excess oxygen than blood at a pH of 7.34. Lack of oxygen and the resulting metabolic acidosis is a component of just about every disease we know.
In today s world, most people s bodies and blood are more acidic than they should be. This is the result of a poor diet (heavy in sugar, soft drinks, excessive protein, and refined carbohydrates), dehydration, stress, and environmental pollutants. Each of these contributes to acidosis and unfortunately also to disease and premature aging.
Oxidation-Reduction Potential (ORP)
antioxidnt
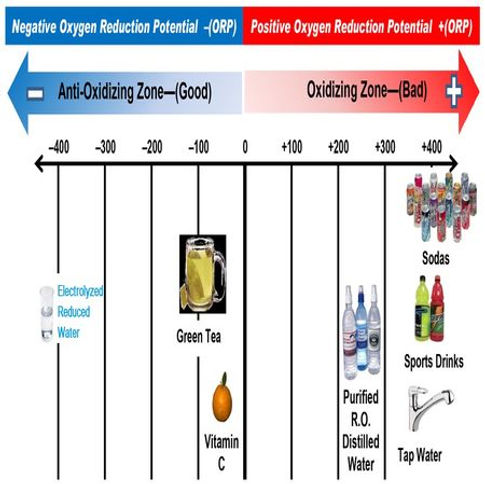
ORP (oxidation/reduction potential) is the second change that occurs to water during Ionization. ORP is a measurement of the strength of the oxidizing or reducing the power of a solution. Oxidation and reduction reactions involve an exchange of electrons. A negative ORP measurement indicates a surplus of electrons the more negative the number is, the greater the number of surplus electrons. A positive ORP measurement indicates instability. A solution with a positive ORP is hungry for electrons.
Most hydrogen in nature is found as hydrogen gas (H²) or as a hydrogen ion (H+), where the electron is absent because the single proton in the nucleus of hydrogen exerts a weak pull to hold onto the electron. Active Hydrogen is a hydrogen atom that holds its electron. This extra electron is electrolysis process nanoparticles created through the electrolysis process during which platinum-coated plates are charged with an electrical current.
Water that is rich in active hydrogen will therefore have a negative ORP. The more negative the ORP value, the more free radical neutralizing electrons the water contains and the stronger its antioxidant properties. This extra electron is able to react with other compounds in the body to control Redox electric field inside the cell and serve as a rich source of antioxidants that can neutralize some of the harmful effects of free radicals, helping to restore the health and balance of the cell.
micro cluster
Micro-Cluster
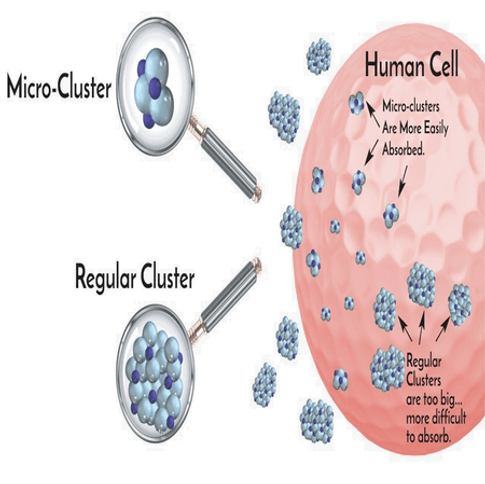
Perhaps one of the most significant features of Electrolyzed Reduced Water (ERW) is its ability to hydrate cells. The precise explanation for this mechanism has not been clearly established. Since we now understand that water penetrates cell membranes through specific protein channels, it is conceivable that in states of oxidative stress these protein pores may become damaged and somewhat dysfunctional. This could theoretically impair cellular hydration. By drinking antioxidant-rich alkaline water, it is not a stretch to be restored to their healthy state, allowing for improved entry of water into the cell, thus allowing optimal cellular hydration.
In 1986, a new theory referred to as the molecular water environment theory was proposed at a symposium on cancer. The theory stated that replenishing the crystalline (hexagonally- structured) water in the human body could increase vitality, slow the aging process, and prevent disease.
The theory was based on research that revealed the following:
-
A greater degree of structure in the water of an infant s body than in the water of an adult s body.
-
A greater degree of structure in the water surrounding healthy DNA than cancerous DNA.
-
A greater degree of structure in the water surrounding the proteins of healthy tissue than in the water surrounding the proteins of cancerous tissue.
-
The ability of structured water to improve bowel transit time and constipation in a clinical trial The ability of structured water to slow the growth of cultured cancer cells.
bottom of page




